Communication via technology would not have been possible without two simple yet essential parts – switches and routers – which empower us to set up networking and connections which travel across the world.
If you are about to start a small business or need to revamp your office, these two apparatuses are key. Let`s take a look at their differences, functions, and purposes.
Switches & Routers – An Overview
If we take an office ambience the most basic workstation related peripherals found apart from computers and laptops are usually servers and printers.
Switches enable all of these resources to link and communicate with each other forming the office network, sharing information allowing employees to work with ease, while interconnecting and liaising with other people also outside of that office area, building or campus.
The process of linking network segments is also called bridging, thus switches are sometimes also referred to as bridging devices, but also bridging hub, switching, or MAC bridge. Furthermore, the efficiency of the switch can be augmented by using a faster network speed.
Creating a small business network without switches is simply impossible as they bond and organise devices together.
Routers on the other hand are also connecting, not multiple devices though, but the switches themselves and their networks forming even a larger network, which can be located in a single site or across numerous ones.
In a business network we will find that apart from switches, one or more routers are needed which apart from connecting various networks together, they will enable several users and networked devices to access the internet.
We can compare a router to a dispatcher, directing traffic while evaluating and selecting which is the most effective route to drive info through in the form of data packets, travelling across a network. Moreover, many routers also contain built-in switches which allow for multiple wired devices to be connected, while we also find that there are routers which hold wireless radios allowing us to connect Wi-Fi devices.
To remain connected to the rest of the world a router is indispensable, and it also protects your information from security threats, while prioritising devices over others.
Main Variances
Going a bit more technical now, we will dive in the switches and routers mechanics and features, basically listing while also spotting their differences.
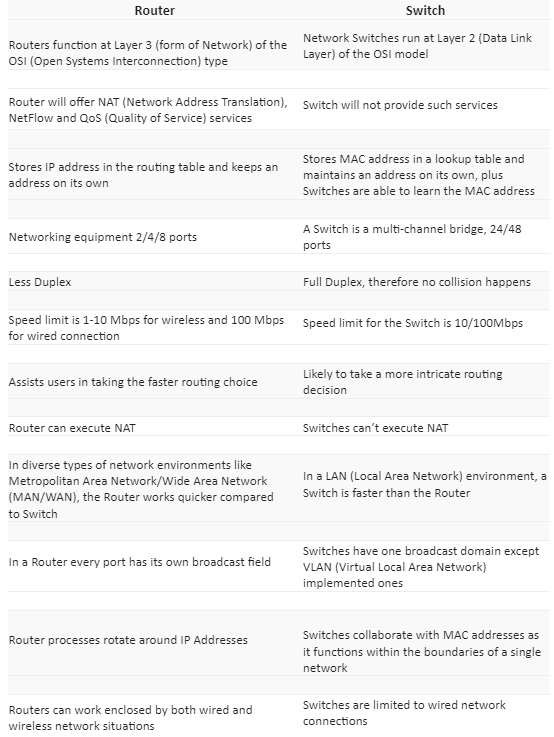
Main Variances
Going a bit more technical now, we will dive in the switches and routers mechanics and features, basically listing while also spotting their differences.
Key Applications
Router
- It permits splitting internet connection to all of your devices
- Links different media/devices with each other
- Runs a firewall
- Routers control where to send info from one computer to another
- Switching, Filtering and Packet Forwarding
- Router also ensures that data does make it to the intended destination
- Connects to Virtual Private Network or VPN
- Generates a local area network (LAN)
Switch
- Switches help us to manage the flow of data across the network
- Medium to large-sized LANs covering a number of linked managed Switches
- Switches are universally used in SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) applications. SOHO mostly uses a single Switch to access the numerous broadband services
- Switch is used in a computer network to link the devices together physically
- A Switch can send data to any of the other devices, either using half-duplex mode or full-duplex mode
Benefits & Drawbacks
Router Advantages
- Data load is lowered as the router allows delivering the packets of data in an organised way
- Router provides a stable and consistent connection between network hosts
- If the main part fails to transfer data packets, Routers make use of the alternative parts
- Productivity is increased by sharing a network connection with multiple machines
Router Disadvantages
- Connections can become slow when several computers are using a network. This situation is defined as a connection wait
- A Router helps numerous computers to share the same network, which may lower the speed
Switch Advantages
- Reduces the number of broadcast domains
- Supports VLAN’s that can assist in Logical segmentation of ports
- Switches can use CAM table for Port to MAC mapping
Switch Disadvantages
- Not as good as a router for restraining broadcasts
- Communication between VLANs necessitates inter VLAN routing, but nowadays there are many multilayer Switches available in the market
- Handling multicast packets that involve quite a bit of arrangement and appropriate designing
- Reduces the number of broadcast domains
In Conclusion
It is vital then that we recognise what switches and routers are for, which to choose for a specific setup being a personal one at our homes or a business framework at the office, and how to attain their full potential while keeping it within our budget.

