Are you new to the world of web hosting and servers? It’s common to come across terms like “host” and “server” but understanding the difference between them is crucial for anyone navigating the online realm. In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll delve into the dissimilarities between hosts and servers, shedding light on their distinct roles in the digital landscape.
With so many individuals and businesses striving to establish their online presence, it’s essential to comprehend the disparities between these two fundamental components. Whether you’re a website owner, a developer, or simply an inquisitive internet enthusiast, this article will provide you with valuable insights and equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your online ventures.
Throughout this post, we’ll clarify the definitions of host and server, explore their core functionalities, and examine how they interact to ensure the smooth operation of websites. By the end, you’ll have a firm grasp of the contrasting aspects of hosts and servers, empowering you to optimize your web presence and enhance user experiences.
Join us as we uncover the intricate details of host and server functionalities, guiding you through the intricacies of these essential components of the online world. Let’s embark on this journey of discovery and demystify the perplexing question: What’s the difference between host and server?
Simply put,
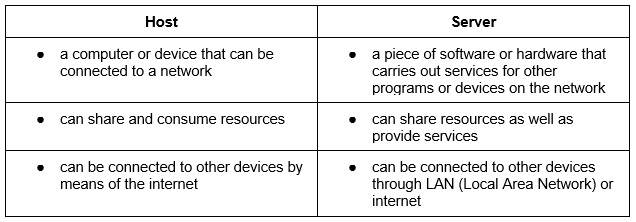
A host is a device that connects to a computer, this could be a computer, laptop, tablet or smartphone.
A server is a piece of hardware or even software that can provide a service to other devices. It can also provide services to programs connected to the network.
To summarise, a host’s role is to share and consume resources found on the network while a server’s role is to provide services, they also share network resources. Both hosts and servers require a network to function effectively and efficiently.
Hmm, still confused? No problem! Here’s an extensive explanation discussing the differences between host and server:
What is a host in a network?
Think of a host as a machine that can be connected to a device within the network. As mentioned above, this could include your personal computer, your work laptop or even your faithful iPhone. This interaction completes a purpose and with the expectations of 21st-century life, we’re constantly connected.
A network, simply put, is a collection of devices – all of which have their own Internet Protocol (IP) address and specific software that allows your devices to communicate and understand instructions.
Whenever a host is displayed with a hostname, the Domain Name System (DNS) converts it to an IP address in order to have seamless translation between devices and networks.
Understood? Great! So let’s go that little bit deeper… not all devices can be considered hosts. Any form of device that does not have its own IP address cannot be classed as a host, this includes; hubs, switches, routers or WiFi boosters.
What is a server?
Understanding what a server is can get complicated, so we’re going to break this down into simple jargon – so everyone can be in the know!
First off, a server can be both software and hardware. Its role is to provide a service to any device that is connected to the network. But, and it’s a big but… not all connected devices are hosts.
Devices using these type of services are called Clients and can also be both hardware or software. A server can serve multiple users at the same time from either the same device or different devices entirely.
Let’s take a closer look at the types of servers on the market.
What are the different types of servers?
The first question you’re probably asking is, “why are there so many servers?” Well, that’s a fair question until you begin to understand the purpose of each server type. Some example of servers could include:
Web Servers
Programs designed for HTML pages or files and we all use this type of server every single day! An easy to understand example is the web browser, be it Google, Yahoo, Bing and anything in between.
Database Servers
These servers manage and store data that is used by other devices connected to the network. Some examples here are: Oracle, Informix, and Microsoft SQL.
Mail Servers
Much like AOL, Gmai and Microsoft Outlook, a mail server holds the purpose of sending and receiving electronic mail, aka e-mails, to a specific recipient. This communication is open to local users and remote senders.
File Servers
A file server is a device that stores and manages data, such as a hard drive or USB. These devices communicate with other devices on the network granting access to the information stored within the file server. Google Drive can also be used as a file server.
Application Servers
These types of servers provide the logic for the app – they are programs in a network that communicate with other devices. Some examples include: Enterprise JavaBean and Java 2 Platform.
In summary, all servers manage and store data in some way, they also share information and order computations. Every server type is intended to carry out a particular purpose in order to ensure seamless operation and connectivity.
Last step and we’re almost done! Here’s a breakdown of the main differences between host and server.
If you’re still finding trouble with a host or a server for your business, contact 4Sight today, our IT experts will guide you in the right direction. Hey, we could even set the whole thing up in no time – it’s what we do!

